Dinosaurs have captured the human imagination for generations, serving as the stars of countless movies, books, and scientific studies. These magnificent creatures roamed the Earth for over 160 million years, from the Triassic period through the Jurassic and into the Cretaceous. Their fossils tell a story of evolutionary triumphs and dramatic extinctions, offering a window into the distant past and the workings of natural history. This blog explores the evolutionary journey of dinosaurs, from their origins to their ultimate extinction, highlighting their significance in our understanding of life's history on Earth.
- Blogs
- History
- The Evolutionary Journey Of Dinosaurs From Origins To Extinction 668d0a75bdccdd0001d30a57
The Evolutionary Journey of Dinosaurs: From Origins to Extinction
History • 9 Jul, 2024 • 24,634 Views • ⭐ 1.0
Written by Shivani Chourasia

Origins of Dinosaurs

The story of dinosaurs begins in the Triassic period, around 230 million years ago. During this time, the supercontinent Pangaea was still intact, and the climate was generally hot and dry. Early dinosaurs evolved from a group of reptiles known as archosaurs, which also gave rise to modern birds and crocodiles. The earliest known dinosaurs, such as Eoraptor and Herrerasaurus, were small, bipedal predators that lived in what is now South America.
These early dinosaurs were part of a diverse ecosystem that included various other reptiles, amphibians, and the first true mammals. Over time, dinosaurs began to diversify and dominate these ecosystems, outcompeting many other groups of animals. This period laid the foundation for the incredible diversity and adaptation that would characterize the dinosaur lineage.
HISTORY QUIZ • 10 QUESTIONS • 2 MINS
We've got a History quiz for you!
TAP TO PLAY

Evolutionary Adaptations
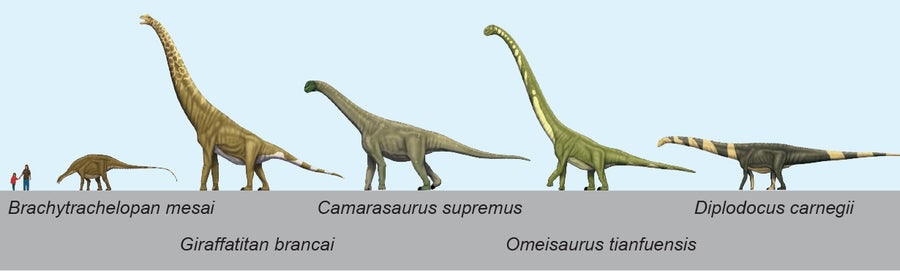
As dinosaurs spread across the globe and occupied various ecological niches, they underwent significant evolutionary changes. These adaptations allowed them to thrive in various environments and contributed to their long-term success. Some of the key evolutionary adaptations of dinosaurs include:
- Body Size and Shape: Dinosaurs evolved a wide range of body sizes and shapes, from the tiny, feathered Microraptor to the colossal Argentinosaurus. This diversity in size and form allowed them to exploit different habitats and food sources.
- Locomotion: Many dinosaurs developed specialized modes of locomotion. Bipedal dinosaurs, such as theropods, walked on two legs and were often fast and agile predators. Quadrupedal dinosaurs, like sauropods, walked on four legs and included some of the largest land animals ever to exist.
- Feathers and Insulation: Evidence suggests that many dinosaurs, especially theropods, had feathers. These feathers were likely used for insulation, display, and possibly even flight in some species. The discovery of feathered dinosaurs has provided crucial insights into the evolution of birds.
- Sensory Adaptations: Dinosaurs had well-developed senses that helped them survive in their environments. For instance, some theropods had keen eyesight and a heightened sense of smell, making them effective hunters.
- Social Behavior: Fossil evidence indicates that some dinosaurs exhibited complex social behaviours, including herd living and parental care. For example, fossilized nests and trackways suggest that certain species, like hadrosaurs, lived in groups and cared for their young.
Diversity of Dinosaurs

The Mesozoic era, often called the Age of Dinosaurs, saw an incredible diversification of dinosaur species. Dinosaurs occupied a variety of habitats, from dense forests to arid deserts, and played multiple ecological roles. Some notable dinosaur groups include:
- Theropods: This group includes famous predators like Tyrannosaurus rex and Velociraptor. Theropods were primarily carnivorous, though some later evolved into omnivores and herbivores.
- Sauropodomorphs: These long-necked herbivores, such as Brachiosaurus and Diplodocus, were among the largest animals ever to walk the Earth. Their massive size allowed them to reach high vegetation and deter predators.
- Ornithischians: This diverse group included herbivorous dinosaurs like Triceratops, Stegosaurus, and Ankylosaurus. Ornithischians often had specialized teeth and jaws for processing plant material and defensive structures like horns and armour.
- Pterosaurs: Although not dinosaurs, pterosaurs were closely related flying reptiles that shared the skies with their terrestrial cousins. Pterosaurs varied greatly in size and adapted to different ecological niches, from fish-eating to insect-catching.
The Dinosaur Renaissance

The 20th century witnessed a resurgence in dinosaur research, often referred to as the Dinosaur Renaissance. This period was marked by numerous groundbreaking discoveries and advancements in palaeontology, reshaping our understanding of dinosaurs. Key developments included:
- Feathered Dinosaurs: The discovery of feathered dinosaurs in China, such as Sinosauropteryx and Archaeopteryx, provided strong evidence for the evolutionary link between dinosaurs and birds. These findings revolutionized our perception of dinosaur biology and behaviour.
- Dinosaur Behavior: New fossil evidence, including nesting sites and trackways, revealed complex social behaviours in dinosaurs. Studies suggested that some species lived in herds, cared for their young, and engaged in sophisticated hunting strategies.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Technologies like CT scanning and 3D modelling allowed scientists to study dinosaur fossils in unprecedented detail. These techniques provided insights into dinosaur anatomy, growth patterns, and even the internal structure of their bones.
- Global Expeditions: Expeditions to previously unexplored regions, such as Patagonia and Mongolia, unearthed a wealth of new dinosaur species. These discoveries expanded our knowledge of dinosaur diversity and distribution.
Extinction Event
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-492602763-56d32ae45f9b5879cc8aa683.jpg)
The end of the Cretaceous period, around 66 million years ago, marked the abrupt extinction of non-avian dinosaurs. This mass extinction event, known as the K-T (Cretaceous-Paleogene) extinction, wiped out approximately 75% of Earth's species. Several theories have been proposed to explain this catastrophic event:
- Asteroid Impact: The most widely accepted theory is that a massive asteroid struck the Yucatan Peninsula in present-day Mexico, creating the Chicxulub crater. This impact would have triggered a chain of catastrophic events, including massive wildfires, tsunamis, and a "nuclear winter" effect caused by dust and aerosols blocking sunlight.
- Volcanic Activity: Extensive volcanic eruptions in the Deccan Traps of India may have contributed to the extinction. These eruptions would have released vast amounts of volcanic gases, leading to climate change and ocean acidification.
- Climate Change: Gradual climate changes, such as cooling temperatures and fluctuating sea levels, could have stressed dinosaur populations and made them more vulnerable to extinction.
- Ecological Competition: The rise of new plant species and the evolution of mammals may have created additional ecological pressures on dinosaurs, contributing to their decline.
While the exact cause of the K-T extinction remains a topic of scientific debate, a combination of these factors likely played a role in the demise of the dinosaurs.
Legacy of Dinosaurs

Despite their extinction, dinosaurs have left an indelible mark on modern science and culture. Their fossils continue to be a source of fascination and inspiration, contributing to our understanding of evolution, biology, and the history of life on Earth. Dinosaurs have also had a significant cultural impact, influencing everything from literature and film to toys and theme parks.
In the realm of science, the study of dinosaurs has advanced our knowledge of ancient ecosystems, evolutionary biology, and the processes of extinction and adaptation. Dinosaurs have become icons of scientific discovery, symbolizing the ever-evolving nature of life on our planet.
Conclusion
The evolutionary journey of dinosaurs, from their origins in the Triassic period to their extinction at the end of the Cretaceous, is a testament to the incredible adaptability and diversity of life. Through their fossils, we can trace the rise and fall of these magnificent creatures, gaining insights into the ancient world they inhabited. The legacy of dinosaurs endures, captivating our imaginations and driving scientific inquiry, reminding us of the dynamic and ever-changing history of life on Earth.
Test your knowledge of History! Visit: https://www.quizzop.com/history-quiz/category
Rate this article
Other articles you may like
Profiles of WWII Leaders: Pivotal Decisions
History • 23 Jan, 2024 • 1,01,181 Views

The Role of Technology in Shaping WWII
History • 23 Jan, 2024 • 1,84,911 Views

WWII Major Battles: Key Events
History • 23 Jan, 2024 • 1,01,361 Views

WWII Origins: Key Causes & Global Impact
History • 23 Jan, 2024 • 99,869 Views

Europe's 7 Most Significant War Memorials
History • 4 Sept, 2023 • 1,42,322 Views





