If you've ever found yourself confused about why your clock changes twice a year, you're not alone. Daylight Saving Time (DST) can seem like a strange and unnecessary tradition, but it has a long history and practical roots. In this blog, we’ll break down the basics of DST in a simple, easy-to-understand way, helping you get a clear idea of what it is, why it was introduced, and the impact it has on our lives today.
What Is Daylight Saving Time (DST)?
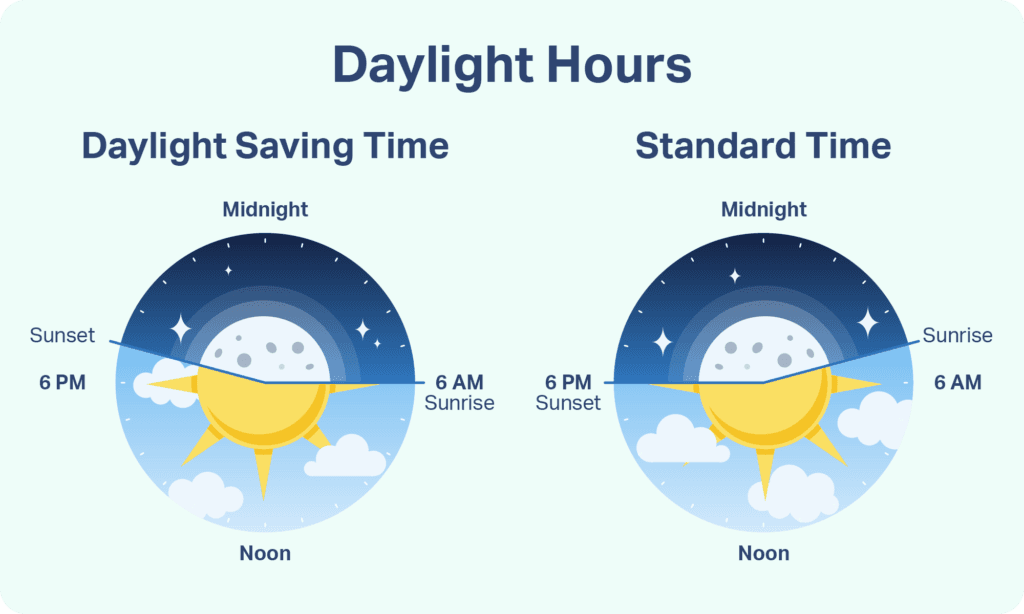
Daylight Saving Time is the practice of moving the clocks forward by one hour during the warmer months (spring and summer) and then moving them back again in the cooler months (fall and winter). The idea behind this practice is to make better use of daylight during the longer days of summer by having more sunlight in the evening, rather than in the early morning when most people are still asleep.
In simple terms, DST is designed to shift an extra hour of daylight from the morning to the evening, allowing us to make the most of daylight during the longer summer days.
Why Was Daylight Saving Time Originally Implemented?

Daylight Saving Time wasn’t always around. The idea was first proposed as a way to conserve energy. By having more daylight in the evening, people would theoretically use less artificial lighting, thus saving electricity. This was particularly relevant in times when energy consumption was a national concern, such as during World War I and World War II. Countries that implemented DST believed it could reduce fuel consumption during wartime by cutting down on the need for evening lighting.
But the idea of adjusting the clocks to match daylight goes back even further. Some sources credit Benjamin Franklin with suggesting something similar in the late 18th century. He reportedly proposed that people wake up earlier in the summer to make better use of natural daylight, but this was more of a humorous suggestion rather than a serious proposal for clock changes.
A Brief History of Daylight Saving Time
The first official use of Daylight Saving Time occurred in Germany in 1916, during World War I. The idea quickly spread to other countries in Europe, and the United States followed suit in 1918. After the wars, many countries discontinued the practice, only to revive it during World War II.
In the U.S., DST became a national standard with the Uniform Time Act of 1966, though states were allowed to opt out. Over time, more regions around the world have adopted or dropped DST based on their specific needs and public opinions.
Today, about 70 countries still observe Daylight Saving Time, including most of Europe and North America. However, many countries near the equator do not use DST because they experience relatively consistent daylight hours year-round.
How Does DST Work?
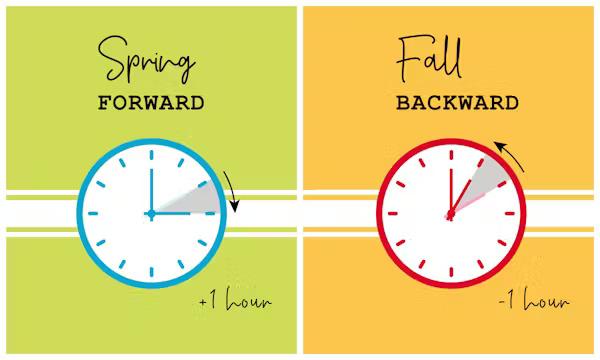
The basic concept of Daylight Saving Time is simple: In the spring, clocks are set forward by one hour (“spring forward”), and in the fall, clocks are set back by one hour (“fall back”). This adjustment is made to take advantage of the extended daylight hours during the summer months.
For example, in the United States, DST begins on the second Sunday of March. At 2:00 AM, clocks are set forward by one hour, meaning that 2:00 AM becomes 3:00 AM. Similarly, DST ends on the first Sunday in November, when clocks are set back an hour at 2:00 AM, effectively turning 2:00 AM into 1:00 AM.
This time shift is designed to allow for more daylight in the evening, which can be especially beneficial in regions where daylight hours fluctuate significantly between seasons. In places where summer days are long and winter days are short, DST can help make evenings brighter and reduce energy consumption during the evening hours.
How DST Affects Daily Life

In theory, DST provides more daylight in the evenings, which can have several practical effects on daily life:
Waking Hours: With more daylight in the evening, people can enjoy outdoor activities after work or school without needing artificial lighting.
Work Schedules: Some industries, particularly those reliant on daylight (like farming or construction), may benefit from extended daylight hours in the evening.
Energy Usage: One of the original arguments for DST was that it could save energy. Longer daylight hours in the evening reduce the need for electricity to light homes and businesses. However, some modern studies suggest the energy savings are minimal, as other factors like air conditioning use may increase during longer days.
That said, DST is not without its drawbacks. One common complaint is the disruption to sleep schedules. When clocks are set forward in the spring, people effectively lose an hour of sleep, which can lead to tiredness and even health issues for some.
The Pros and Cons of Daylight Saving Time

Like most things in life, Daylight Saving Time has its pros and cons. Let’s take a look at both sides of the argument:
The Benefits of Daylight Saving Time:
More Daylight in the Evenings: DST allows for longer evenings with more sunlight, which can encourage people to spend more time outdoors and engage in recreational activities.
Potential Energy Savings: Although modern studies show mixed results, the original goal of DST was to conserve energy by reducing the need for artificial lighting in the evenings.
Boost to the Economy: Longer daylight hours can be beneficial for certain businesses, especially those that rely on evening activities, like restaurants, retail stores, and entertainment venues.
The Downsides and Controversies of DST:
Sleep Disruption: The time change, particularly in the spring, can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, leaving people tired and less productive.
Health Risks: Some studies suggest that the shift in time may lead to an increase in heart attacks, strokes, and accidents, especially in the days immediately following the time change.
Is It Still Necessary? In our modern world, where energy-efficient technologies are widely available, many question whether DST still serves its original purpose of conserving energy. Some argue that the practice is outdated and should be abolished.
Why Some Countries Have Abandoned DST

Not all countries observe Daylight Saving Time, and some have chosen to abolish it altogether. For example, Russia discontinued DST in 2011, citing health concerns related to the time changes. Similarly, countries near the equator, where daylight hours remain consistent year-round, often don’t see the need for DST at all.
In contrast, other countries continue to observe DST, seeing the benefits of longer daylight hours in the evening. In the U.S., there has been ongoing debate about whether DST should be extended year-round, a practice known as “permanent Daylight Saving Time.”
Will DST Continue or Be Phased Out?

The future of Daylight Saving Time remains uncertain. While some regions continue to support the practice for its economic and lifestyle benefits, others argue that the drawbacks, particularly in terms of health and sleep disruption, outweigh the advantages.
In recent years, there has been growing momentum to eliminate the biannual clock changes and adopt a permanent time system. For now, however, DST remains a widely observed practice in many parts of the world.
Conclusion
Daylight Saving Time, while confusing at times, was originally introduced as a way to conserve energy and make better use of daylight. Over the years, it has become a staple in many countries, though not without its share of controversy. As we continue to weigh the pros and cons, the future of DST is uncertain, but for now, we’ll keep “springing forward” and “falling back” as we have for over a century. Ultimately, whether you love or hate it, DST is one of those quirks of modern life that continues to impact our daily routines, at least for the foreseeable future.
Test your General Knowledge! Visit:https://www.quizzop.com/general-knowledge-quiz/category


